SOTDMA and CSTDMA
Section 1. SOTDMA
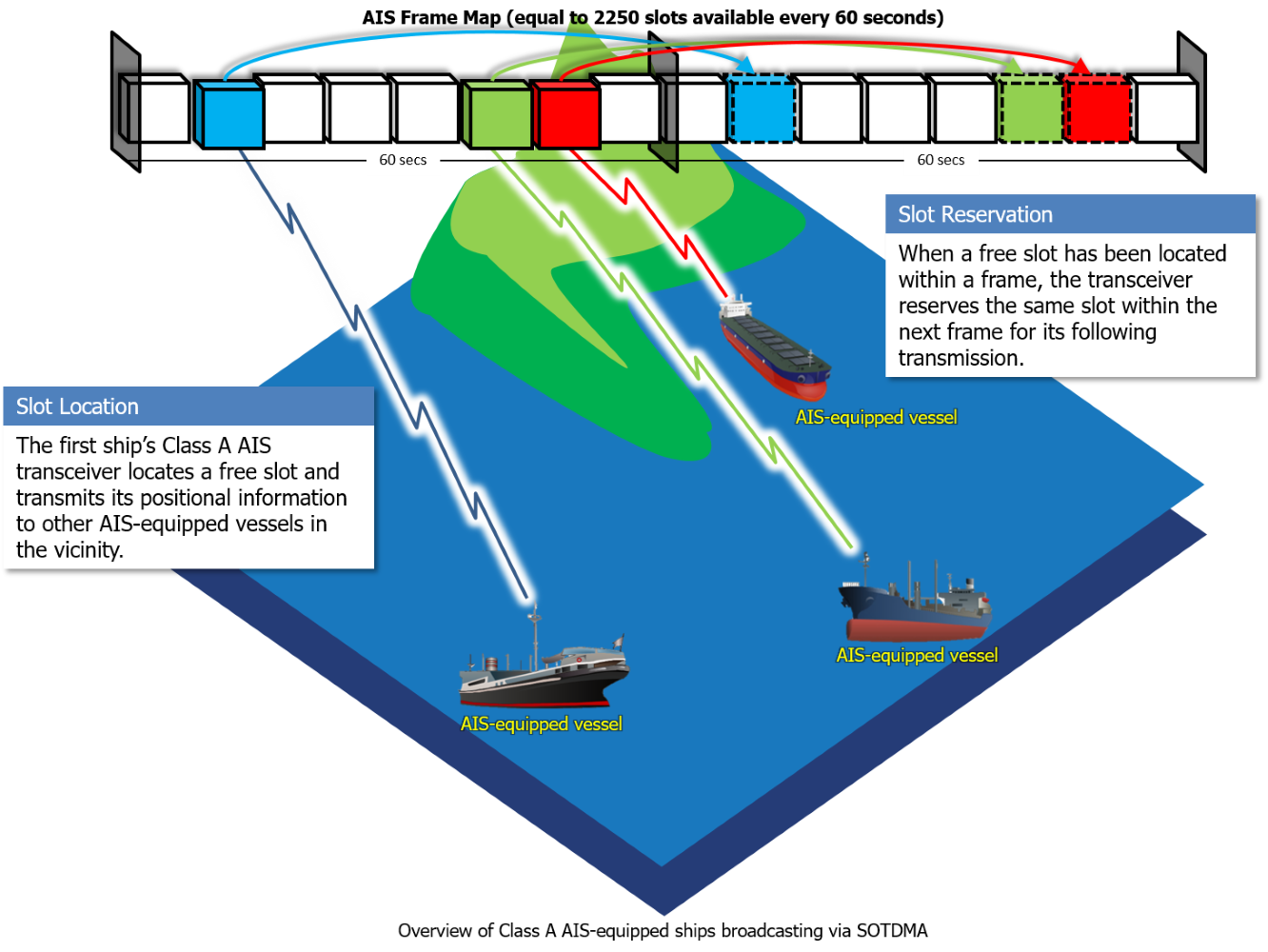
Self-Organizing Time-division Multiple Access, or SOTDMA (sometimes referred to as STDMA), is a TDMA access scheme designed for Class A AIS devices. As opposed to TDMA, which requires a central station for time synchronization and to assign slots to the users trying to broadcast, SOTDMA permits users to scan for and reserve their own slots. All users operating on SOTDMA will use Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) as the common time reference.
Through SOTDMA, a Class A AIS device will scan for available and “un-reserved” slots in the AIS slot frame map (one frame is equal to 2250 slots available in one minute intervals, frame maps are sometimes referred to as “slot maps”), avoiding slots that it perceives to be occupied in order to prevent conflicts with other broadcasting stations. Once it locates a free slot, the transceiver will reserve it and transmit over it. It will also reserve the slot within the following frame for the next transmission so long as the ship is using the same frame map.
As the ship moves into new areas and encounters other ships, it will also encounter a new AIS slot map, which will have a different AIS slot map allocation based on what the other ships have reserved. The transceiver will continue to scan for available slots on each new map it joins.
Section 2. CSTDMA
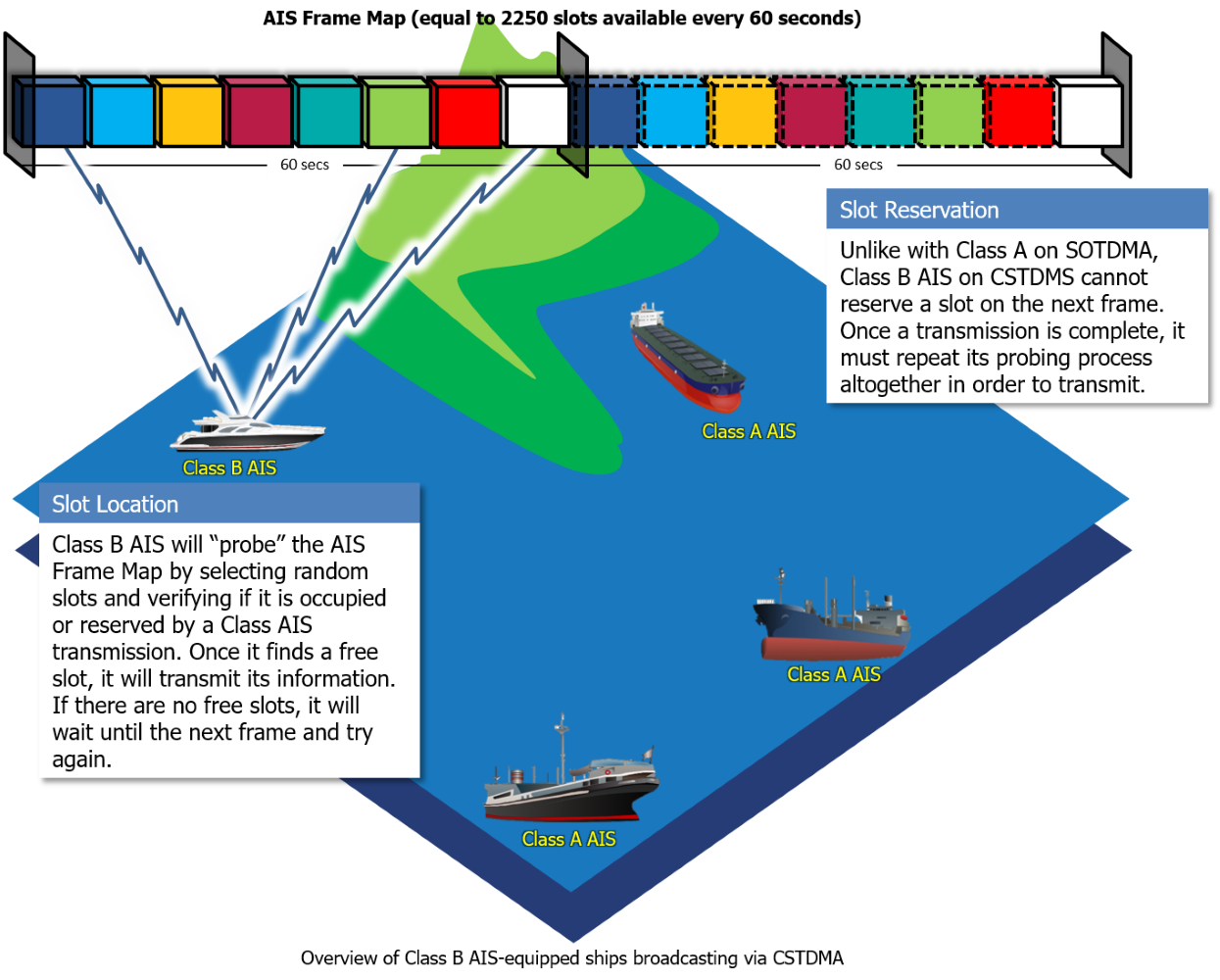
Carrier-Sense Time division Multiple Access, or CSTDMA, is a TDMA access scheme designed for Class B AIS transceivers. It permits ships with Class B transceivers to exchange AIS information on the same AIS Frame Map used by Class A AIS devices broadcasting via SOTDMA.
Ships broadcasting AIS using CSTDMA continuously monitors the background noise level on AIS radio channels while at the same time selecting and “listening in” on random slots on the AIS Frame Map. If the randomly selected slot emits a signal that is “louder” than the background noise, the Class B AIS transceiver will assume the slot is taken and will randomly select another slot. Once it finds a slot whose signal strength is close to the background noise, the Class B transceiver will assume that the slot is free and broadcast its AIS data. The transceiver must repeat this process for every broadcast as CSTDMA does not permit Class B AIS devices to reserve slots on future frames. This ensures that Class A transceivers are always guaranteed priority on the AIS Frame Map in order to maintain safety in navigation.
References and further reading
Additional technical information on SOTDMA and CSTDMA can be found in Annexes 2 and 7 respectively of International Telecommunication Union’s Recommendation M.1371-5 – Technical characteristics for an automatic identification system using time division multiple access in the VHF maritime mobile frequency band.
Report a problem on this page
- Date modified: